19.2 Segregation
Mendel’s model organism
Mendel’s work was accomplished using the garden pea, Pisum sativum, to study inheritance. This species naturally self-fertilizes, such that pollen encounters ova (egg cells) within individual flowers. The flower petals remain sealed tightly until after pollination, preventing pollination from other plants. The result is highly inbred, or “true-breeding,” pea plants. These are plants that always produce offspring that look like the parent. By experimenting with true-breeding pea plants, Mendel avoided the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring that might occur if the plants were not true breeding. The garden pea also grows to maturity within one season, meaning that several generations could be evaluated over a relatively short time. Finally, large quantities of garden peas could be cultivated simultaneously, allowing Mendel to conclude that his results did not come about simply by chance.
Mendelian Crosses
Mendel performed hybridizations, which involve mating two true-breeding individuals that have different traits. In the pea, which is naturally self-pollinating, this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety. In plants, pollen carries the male gametes (sperm) to the stigma, a sticky organ that traps pollen and allows the sperm to move down the pistil to the female gametes (ova) below. To prevent self-fertilization in the pea plant that was being manually fertilized using pollen from the second parent, Mendel painstakingly removed all of the anthers from the plant’s flowers before they had a chance to mature.
Plants used in first-generation crosses were called P0, or the parental generation. After each cross, Mendel collected the seeds produced by the P0 plants and grew them the following season. These offspring were called the F1, or the first filial (filial = offspring, daughter or son) generation. Once Mendel examined the characteristics in the F1 generation of plants, he allowed them to self-fertilize naturally. He then collected and grew the seeds from the F1 plants to produce the F2, or second filial, generation. Mendel’s experiments extended beyond the F2 generation to the F3 and F4 generations, and so on, but it was the ratio of characteristics in the P0−F1−F2 generations that were the most intriguing and became the basis for Mendel’s postulates.
Mendelian Cross Results
In his 1866 publication, Mendel reported the results of his crosses involving seven different characteristics, each with two contrasting traits. A trait is defined as a variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic. The characteristics included plant height, seed texture, seed color, flower color, pea pod size, pea pod color, and flower position. For the characteristic of flower color, for example, the two contrasting traits were white versus violet. To fully examine each characteristic, Mendel generated large numbers of F1 and F2 plants, reporting results from 19,959 F2 plants alone. His findings were consistent for each of the seven characteristics he studied.
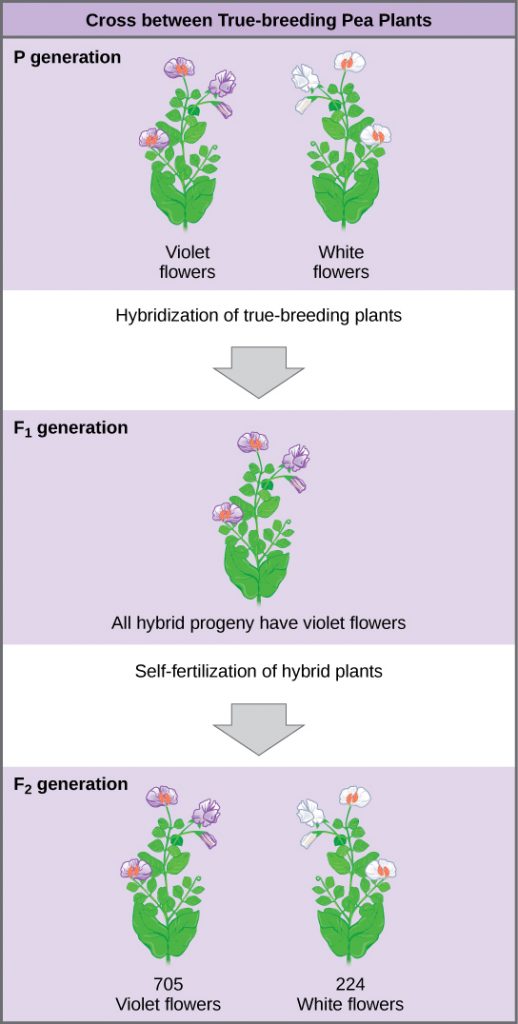
What results did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color? First, Mendel confirmed that he had plants that bred true for white or violet flower color. Regardless of how many generations Mendel examined, all self-crossed offspring of parents with white flowers had white flowers, and all self-crossed offspring of parents with violet flowers had violet flowers. In addition, Mendel confirmed that, other than flower color, the pea plants were physically identical.
Once these validations were complete, Mendel applied the pollen from a plant with violet flowers to the stigma of a plant with white flowers. After gathering and sowing the seeds that resulted from this cross, Mendel found that 100 percent of the plants in the F1 hybrid generation had violet flowers. Conventional wisdom at that time (the blending theory) would have predicted the hybrid flowers to be pale violet or for hybrid plants to have equal numbers of white and violet flowers. In other words, the contrasting parental traits were expected to blend in the offspring. Instead, Mendel’s results demonstrated that the white flower trait in the F1 generation had completely disappeared.
Mendel then allowed the F1 plants to self-fertilize and found that, among the F2-generation plants, 705 had violet flowers and 224 had white flowers. This was a ratio of 3.15 violet flowers per one white flower, or approximately 3:1. Mendel obtained about the same ratio regardless of which parent, male or female, contributed which trait. For the other six characteristics Mendel examined, the F1 and F2 generations behaved in the same way as they had for flower color. One of the two traits would disappear completely from the F1 generation only to reappear in the F2 generation at a ratio of approximately 3:1.
Pairs of Factors, or Genes
Mendel proposed first that paired unit factors of heredity were transmitted faithfully from generation to generation by the dissociation and reassociation of paired factors during gametogenesis and fertilization, respectively. After he crossed peas with contrasting traits and found that the recessive trait resurfaced in the F2 generation, Mendel deduced that hereditary factors must be inherited as discrete units. This finding contradicted the belief at that time that parental traits were blended in the offspring.
Alleles Can Be Dominant or Recessive
Mendel’s law of dominance states that in a heterozygote, one trait will conceal the presence of another trait for the same characteristic. Rather than both alleles contributing to a phenotype, the dominant allele will be expressed exclusively. The recessive allele will remain “latent” but will be transmitted to offspring by the same manner in which the dominant allele is transmitted. The recessive trait will only be expressed by offspring that have two copies of this allele, and these offspring will breed true when self-crossed.
Since Mendel’s experiments with pea plants, researchers have found that the law of dominance does not always hold true. Instead, several different patterns of inheritance have been found to exist.
Equal Segregation of Alleles
Observing that true-breeding pea plants with contrasting traits gave rise to F1 generations that all expressed the dominant trait and F2 generations that expressed the dominant and recessive traits in a 3:1 ratio, Mendel proposed the law of segregation. This law states that paired unit factors (genes) must segregate equally into gametes such that offspring have an equal likelihood of inheriting either factor. For the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross, the following three possible combinations of genotypes could result: homozygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive. Because heterozygotes could arise from two different pathways (receiving one dominant and one recessive allele from either parent), and because heterozygotes and homozygous dominant individuals are phenotypically identical, the law supports Mendel’s observed 3:1 phenotypic ratio. The equal segregation of alleles is the reason we can apply the Punnett square to accurately predict the offspring of parents with known genotypes. The physical basis of Mendel’s law of segregation is the first division of meiosis, in which the homologous chromosomes with their different versions of each gene are segregated into daughter nuclei. The role of the meiotic segregation of chromosomes in sexual reproduction was not understood by the scientific community during Mendel’s lifetime.
parental generation
first filial generation in a cross; the offspring of the parental generation
second filial generation produced when F1 individuals are self-crossed or crossed with each other
trait which confers the same physical appearance whether an individual has two copies of the trait or one copy of the dominant trait and one copy of the recessive trait
trait that appears “latent” or non-expressed when the individual also carries a dominant trait for that same characteristic; when present as two identical copies, the recessive trait is expressed
paired unit factors (i.e., genes) segregate equally into gametes such that offspring have an equal likelihood of inheriting any combination of factors
having two identical alleles for a given gene on the pair of homologous chromosomes
having two different alleles for a given gene on the pair of homologous chromosomes