22.2 Chemiosmosis and ATP Synthase
The hydrolysis of ATP produces ADP, together with an inorganic phosphate ion (Pi), and the release of free energy. To carry out life processes, ATP molecules are continuously being broken down into ADP, and like a rechargeable battery, ADP is continuously being regenerated into ATP by the reattachment of a third phosphate group. Water, which was broken down into its hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group (hydroxide) during ATP hydrolysis, is regenerated when a third phosphate is added to the ADP molecule, reforming ATP.
Obviously, energy must be infused into the system to regenerate ATP. Where does this energy come from? In nearly every living thing on Earth, the energy comes from the metabolism of carbohydrates , especially glucose, fructose, or galactose, which all have the chemical formula C6H12O6 but different molecular configurations.
Most of the ATP generated during glucose catabolism and during photosynthesis is derived from a process called chemiosmosis. Chemiosmosis takes place in the mitochondria, in chloroplasts, and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes to produce ATP.
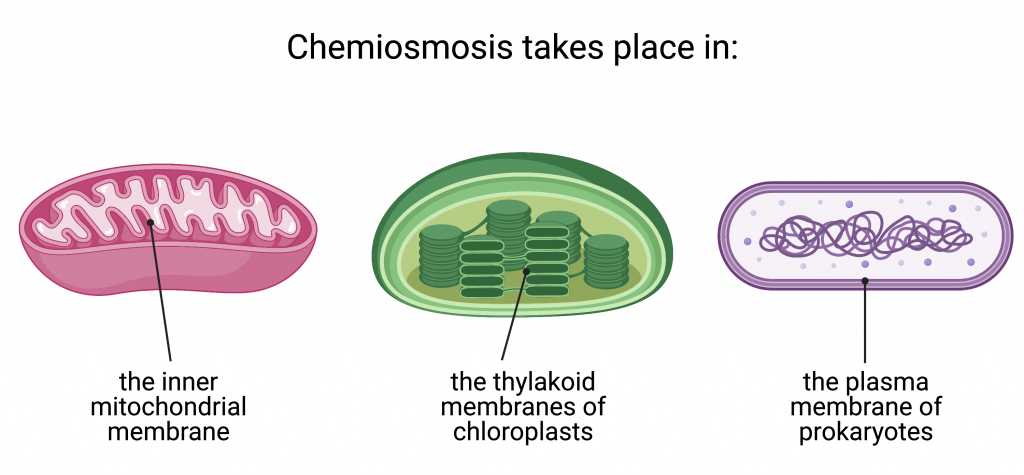
Chemiosmosis
In chemiosmosis, the energy released by the exergonic process of hydrogen ions flowing down their gradient across a membrane is coupled to an endergonic reaction — the regeneration of ATP. Chemiosmosis requires that there is a gradient of protons (i.e. hydrogen ions), otherwise diffusion would not take place.
Recall that many ions cannot diffuse through the nonpolar regions of phospholipid membranes without the aid of ion channels. During chemiosmosis, hydrogen ions pass through a membrane by an integral membrane protein complex called ATP synthase. This complex protein acts as a tiny generator, turned by the force of the hydrogen ions diffusing through it, down their gradient. The turning of parts of this molecular machine facilitates the addition of a phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP, using the potential energy of the hydrogen ion gradient.
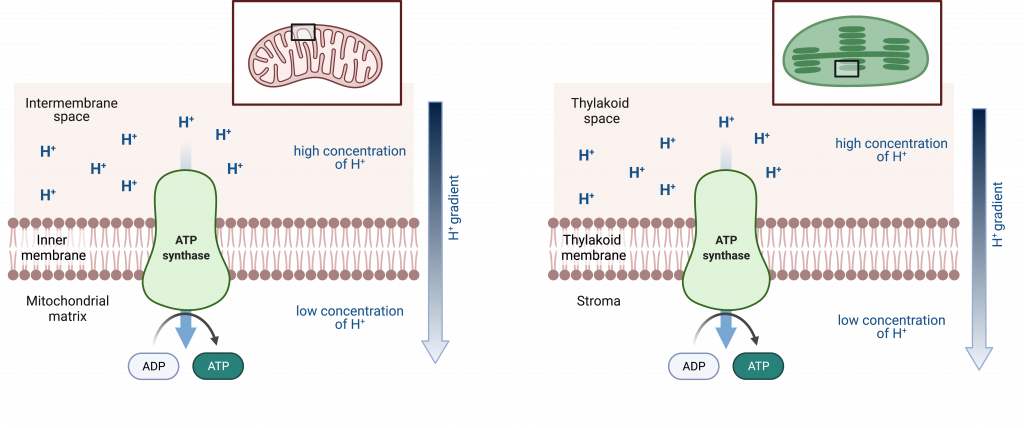
Chemiosmosis is used to generate more than 80 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism; it is also the method used in the light reactions of photosynthesis to harness the energy of sunlight to produce ATP that can then be used to build a carbohydrate.
movement of ions down their gradient through a membrane protein; usually refers to the process that produces ATP by harnessing the energy of protons flowing down their gradient which powers ATP synthase