8.1 Metabolic Pathways
Metabolism
Cellular processes such as building and breaking down complex molecules occur through stepwise chemical reactions. Some of these chemical reactions are spontaneous and release energy; whereas others require energy to proceed. Just as living things must continually consume food to replenish what they have used, cells must continually obtain more energy to replenish that which the many energy-requiring chemical reactions use. All of the chemical reactions that transpire inside cells, including those that use and release energy, are the cell’s metabolism.
Anabolic and Catabolic Pathways
A metabolic pathway is a linked series of biochemical reactions that convert a molecule or molecules, step-by-step, through a series of metabolic intermediates, into a final product or products.
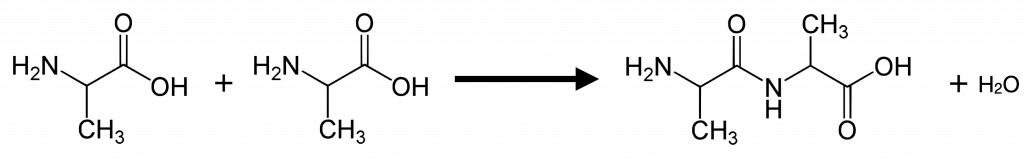
Anabolic pathways require an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones. Synthesizing sugar from CO2 during photosynthesis is one example. Other examples are synthesizing large proteins from amino acid building blocks, and synthesizing new DNA strands from nucleic acid building blocks. These biosynthetic processes are critical to the cell’s life, take place constantly, and demand energy that ATP and other high-energy molecules provide.
Catabolic pathways involve degrading (or breaking down) complex molecules into simpler ones. An example of a catabolic pathway is the breakdown of glucose during cellular respiration. Molecular energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose are harvested in such a way that it can produce ATP. Other energy-storing molecules, such as fats, also break down through similar catabolic reactions to release energy and make ATP.
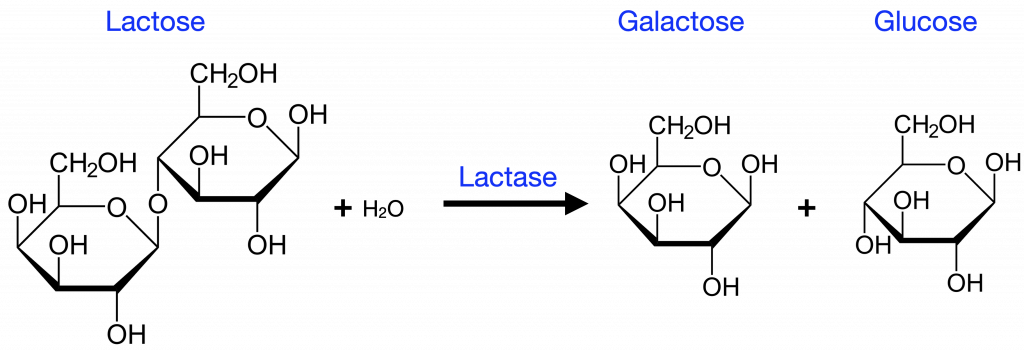
It is important to know that many of the chemical reactions that together constitute a metabolic pathway require a protein called an enzyme to facilitate or catalyzes each step. Enzymes are important for catalyzing all types of biological reactions—those that require energy as well as those that release energy.
all the chemical reactions that take place inside cells
reaction or pathway that requires an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler molecules
the energy currency molecule of cells; provides energy for most biological reactions that require an input of energy
reaction or pathway in which complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones, releasing energy
a biomolecule (usually a protein) that catalyzes chemical reactions
speed up