7.1 Protein Function
Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems. About half of the dry weight of a cell is protein. Proteins have the most diverse range of functions of all the macromolecules. They are the main molecules that carry out the functions of the cell.
The major reason that proteins are so varied in their function is due to their ability to bind other molecules. Various proteins can bind other proteins, DNA, RNA, lipids, carbohydrates, ions, or small molecules. Proteins are specific in their binding abilities; meaning certain proteins can only bind to certain molecules. The generic name for a molecule that a protein binds is ligand, and the place on the protein where it binds is the binding site.
The ability to specifically bind other molecules is a characteristic of a protein’s shape.
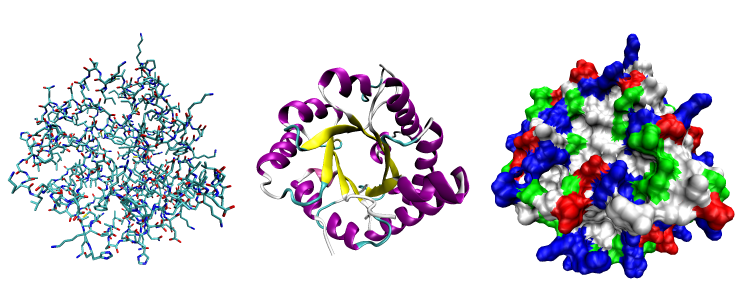
Proteins may be structural, regulatory, contractile, or protective. They may serve in transport, storage, communication, or defense; or they may be toxins or enzymes. Each cell in a living system contains thousands of different proteins, each with a unique function. Their structures, like their functions, vary greatly, but they are all amino acid polymers arranged in a linear sequence.
Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes, which attach amino acids together to form a polypeptide, which folds into its three-dimensional shape.
biological macromolecule made of amino acids; essential for cellular function
a molecule that binds to a protein
the region of a protein that binds another molecule
cellular structure that synthesizes proteins