11 Lab Protocol: Enzymes
Exercise 1: Control experiment to observe amylase activity on starch
At the concentration of amylase you are given by your instructor, the hydrolysis of starch into sugars occurs very quickly. You will perform an experiment to observe this activity by running an experiment at room temperature in a pH=7 buffer.
- Read all the steps in this procedure and write down your hypothesis for the experiment you will test in your data sheet.
- Prepare spot plate with 1 drop of iodine solution in two different wells. Label wells + and -.
- Assemble the following ingredients (from left to right mixing after each addition) that have each been incubated at room temperature.
- Start your timer immediately after you add the amylase enzyme and give the tube a quick mix by shaking it gently.
- Remove 100 µL from each tube at time = 5 minutes and add to appropriate well with iodine solution.
- Record color in table above and take a photograph.
| Tube | pH buffer | Starch solution | Water | Amylase enzyme | Color at 1 min |
| Control (C) | 0.5 mL pH 7 | 0.5 mL | 0.5 mL | 0 µL | |
| Experiment (E) | 0.5 mL pH 7 | 0.5 mL | 0.4 mL | 0.1 mL = 100 µL |
Exercise 2: Preparing serial dilutions of the enzyme amylase
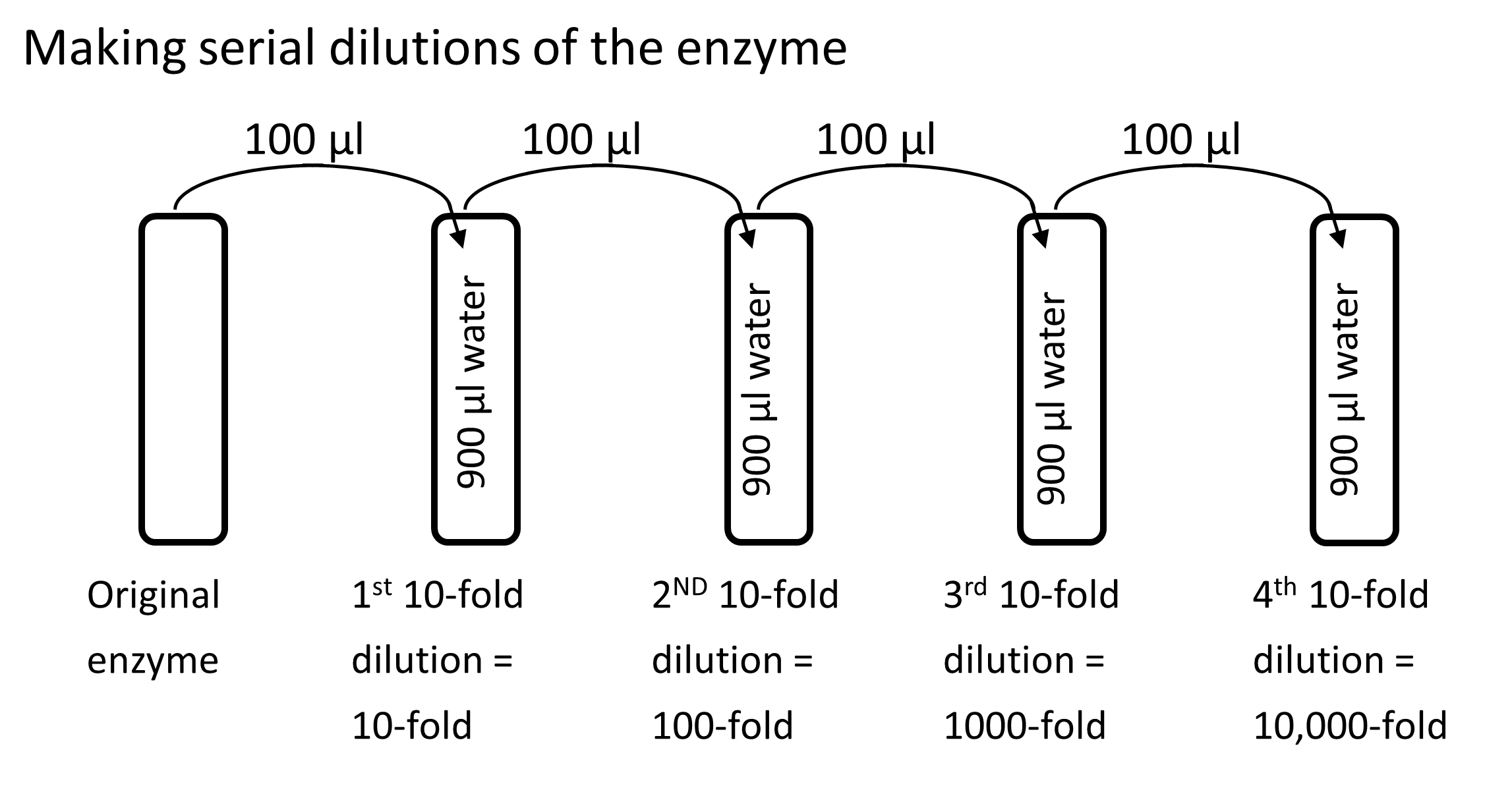
- Label Eppendorf tubes: 1, 2, 3 and 4 to make 1 mL of each dilution. These will be your 10-fold, 1000-fold, and 10,000-fold dilutions according to the diagram below. Note: Best to add appropriate volume of water to each tube first using same pipette tip.
- Prepare the 10-fold dilution by adding 100 ul from the original enzyme solution to the first tube and mixing well by pipetting up and down.
- Use a new pipette tip and take 100 ul from Tube 1 and place it into Tube 2 and mix well by pipetting up and down. Repeat this process for the remaining two dilutions mixing and changing your pipette tip in between.
|
|
10-fold dilution tube |
100-fold dilution tube |
1000-fold dilution |
10,000-fold dilution |
|
Tube Label |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
water |
900 µl |
900 µl |
900 µl |
900 µl |
|
enzyme |
100 µl 1X enzyme |
100 µl 10-fold dilution of enzyme |
100 µl 100-fold dilution of enzyme |
100 µl 1000-fold dilution of enzyme |
Exercise 3: Test the effect of concentration on enzyme activity
The next part of this experiment is to test the rate of the reaction of amylase on the hydrolysis of starch. The goal of this exeperiment is to find a concentration of amylase that will be suitable to run your experiments to test the effect of various physical factors like pH and temperature. Now that you’ve prepared four different dilutions of the enzyme, you will run an experiment to see how long it takes amylase to break down starch at various concentrations starting from your 10X dilution.
- Prepare two spot plates with 1 drop iodine in every well. Make sure they are labelled correctly and take a photo of your spot plate set up.
- Set up a control (-) test tube and and experimental (+) test tube as you did in exercise 1. Add water, buffer, and starch to each tube. You will repeat this process for each of the concentrations you prepared in Exercise 2.
- Add the enzyme to the (+) tube and start your timer.
- Every minute, you will remove 100 µL and add to a fresh well on the spot plate containing iodine. Stop taking samples from the reaction tube once the color in the well stays yellow.
- Take a photograph of the spot plate being sure that the different wells have been labeled. Record your results on your Student Data Sheet.
Exercise 4: Designing an experiment to determine the effect of pH on enzyme activity
This week, you will have more autonomy as budding scientists. You get to plan your own procedure to test the effect of temperature or the effect pH on amylase activity. In this experiment, you will repeat procedures from Exercise 1 and 3. In those experiments, you used a buffer with a pH of 7. Now you will test the rate of amylase activity using different pH levels.
- Discuss with your group how you will run the experiement at 3 additional pH values. There are several different buffer solutions for you to use.
- Run your experiments and record your results in your Student Data Sheet.
- Mix the buffer, water and +/-enzyme and pre-incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes. We will not pre-incubate the starch solution because pH alone might cause starch breakdown.
- You will have the following buffer pH 3, pH 5, pH 7, pH 9, pH 11
First state your hypothesis (explain what you think will happen and why).
Exercise 5: Designing an experiment to determine the effect of temperature on enzyme activity
In this experiment, you will repeat procedures from Exercise 1 and 3. In those experiments, you ran the experiments at room temperature. In this exercise, you will run the experiment at different temperatures. There are 3 different water baths for you to use.
- Discuss with your group how you will run the experiement at 3 additional temperature values.
- Run your experiments and record your results in your Student Data Sheet.
- You will have the following reagents and equipment:Water baths at the following temperatures: 5 C (ice bath) 37 C, 60 C, 80 C.Spot plates, iodine solution, starch solution, pH 7 buffer solution, water, amylase enzyme dilutionTest tubes, P1000 and P200 Micropipettes and tips, waste beaker, grease pencilFirst state your hypothesis (explanation of what you think will happen and why.)
Exercise 6: Engaging in the scientific process
Share your data with your peers and compare your results.